Best Home Loan: How to Maximize Benefits in New Interest Rate Regime
Find out how to select the right lender and optimize benefits under the new regime.
On October 1, all banks shifted to the Reserve Bank of India mandated external benchmarks for pricing their new home loans. While banks have chosen to keep it a low-key affair, for retail borrowers, a shift to loans linked to an external benchmark holds more potential than any other benchmarking mechanism implemented so far. Read on to understand how you can get the best out of the new regime.
The Rationale
For long, a major grouse of home loan borrowers were their lenders’ tendency to increase lending rates in line with RBI’s policy rate hike but drag their feet when it came to pass on rate cut benefits. Existing borrowers also frequently came across banks offering lower rates to attract new borrowers.
Several benchmarking regimes introduced by the banking regulator over the years in a bid to change the situation have met with limited success. These include Prime Lending Rate (PLR), Benchmark Prime Lending Rate (BPLR), Base Rate and Marginal Cost of Funds-Based Lending Rate (MCLR). “For more than 20 years after the RBI deregulated lending rates of banks, the absence of smooth transmission remained a matter of concern,” the apex bank noted in an addendum to the report of its Internal Study Group. The group observed that internal benchmarks such as the Base Rate and MCLR have not delivered effective transmission of monetary policy. It recommended a switchover to an external benchmark to plug this gap.
The
case for an external benchmark
Internal
benchmarks did not keep pace with RBI’s repo rate.


Note: Base Rates were in effect till the introduction of MCLR. Source: ETIG
Banks have often cited the higher internal cost of funds as a key reason for not being able to ensure complete policy transmission. RBI reduced policy rates cumulatively by 110 bps between February and August 2019. Banks, however, reduced interest rates on new loans by just 29 bps during the period. This was noted by RBI in its monetary policy review on 4 October. It said monetary transmission “remained staggered and incomplete.” In fact, lending rates on outstanding loans increased by 7 bps during the same period. This prompted RBI to initially nudge banks to move to an external benchmark to price their loans and finally mandate a switchover for all new retail floating-rate loans from 1 October. Earlier, the shift, proposed to be effective from 1 April, was delayed due to concerns expressed by banks. The new system will not be applicable to housing finance companies regulated by the National Housing Bank (NHB).
The central bank has now allowed banks to choose between the repo rate, 3 or 6-month treasury bills or any other benchmark market interest rate published by the FBIL. However, most banks have picked the repo rate as their external benchmark. “As the repo rate is stable and does not change frequently, most banks are benchmarking their floating rate loans to it,” says Soumya Kanti Ghosh, Group Chief Economic Adviser, SBI. The T-Bill-linked rates could be more volatile (see graphic), say, experts. “Moreover, they will be market-driven, while the repo rate will be driven by the regulator. Repo rate also scores over the T-bill rate in terms of awareness amongst lay individuals. This is a plus from the transparency standpoint,” says Vipul Patel, Founder, Mortgage World.
The effective interest rate will include the spread decided by individual banks
Borrowers will benefit if they opt for loans that come with a narrower spread and transparent credit assessment.
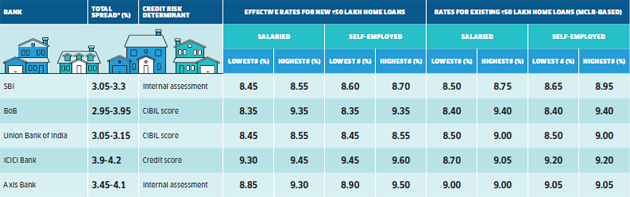

Note: Most banks, except Citibank, have chosen RBI’s repo rate (5.4%) as their external benchmark, Citi’s benchmark is 3-month T-bill rate (5.32% on 1 October); all rates as on 1 October.
RBI reduced its repo rate by 25 bps on 4 October; banks will have to follow suit.
Over the external benchmark rate; in addition, some banks offer 5 bps concession to women borrowers. Rates will also be influenced by the borrower’s credit assessment by the bank. Source: Bank websites, Paisabazaar and Mortgage World.
External
benefits
Your
effective interest rate will be repo rate plus a spread as decided by
banks. “The new effective rate would be repo rate + (negative carry
on CRR + operating cost) + credit risk premium,” explains Ghosh.
Banks will have to reset the rates every three months. “Other
components of the spread including operating cost can be altered once
in three years. However, credit risk premium may undergo change only
when the borrower’s credit assessment undergoes a substantial
change, as agreed upon in the loan contract,” the RBI circular
mandating the move says.
For example, the State Bank of India charges a spread of 265 points over the repo rate (5.4%) for a loan of up to Rs 30 lakh. In addition, a 15 bps credit risk premium comes into play for borrowers with the best internal risk grades (RG 1, 2, 3). Depending on the source of income (salaried or nonsalaried), the loan amount and internal risk grading, the credit risk spread can be as wide as 75 bps. Women borrowers are offered a 5 bps concession on interest rates.
The initial experience of SBI’s report lending rate loan scheme introduced voluntarily in July was encouraging. A 35 bps repo rate cut in August resulted in an equivalent reduction in the product— now withdrawn and replaced with a revised scheme—rate.
An unkind cut for borrowers
Banks were slow in passing on RBI policy rate cuts except after demonetization.


Note: #Existing loans and new loans | ^WALR: Weighted Average Lending Rate for banks | MCLR: Marginal Cost of Funds based Lending Rate. | *: MCLR system was put in place on April 1, 2016. Source: Reserve Bank of India.
On the flip side, as banks have pointed out, borrowers run the risk of frequent increases in their interest outgo or EMIs when the rate cycle turns and RBI starts raising rates.
However, floating-rate borrowers sign up for revision in loan rates depending on interest rates in the system. Therefore, as long as borrowers are aware of this fact at the time of loan approval, the rate movement should not result in shocks.
Devil in the details
Now that most banks have a uniform benchmark, will choose a lender to become easier? Not quite. For one, the spreads charged by banks vary, making it a key determinant in selecting a lender. “It is best to go with a bank that charges the narrowest spread over the repo rate. The interest rate will then be most reflective of the external benchmark rate,” says Ratan Chaudhury, Head, Home Loans, Paisabazaar.com.
This apart, the credit risk component holds the key to this system’s success– it can make or mar the newest effort to get banks to transmit monetary policy fully. “Transparency in risk scoring and borrowers’ ability to understand and verify the same will be critical,” says Patel.
Why repo rate scores over T-bill
Treasury bill-linked home loan rates could be more volatile.


Do note that not all banks have disclosed the credit-risk-premium component of the spread separately. While banks like SBI, Union Bank and Syndicate Bank have specified the credit risk premium, over and above the base spread, some like ICICI Bank, Axis Bank, and Citibank have not. Axis Bank’s website states that the total spread over the repo rate is between 3.45-3.9% for salaried borrowers. ICICI Bank mentions a total spread between 3.9-4.05% for the category. Moreover, while Union Bank and Syndicate Bank have decided to adopt the CIBIL score to determine risk, ICICI Bank mentions that rates will vary based on the “bureau score.” “Clarity is yet to emerge on the credit risk component for all banks. Borrowers will have to enquire before signing loan contracts or wait till the picture is clearer,” says Patel
Then, you need to look at how risk scoring is being arrived at. “Banks may play on credit risk premium, as internal assessments are confidential,” says V.N. Kulkarni, a retired banker, and financial counselor. “The concern is that banks could use this tool to avoid passing on an RBI rate cut, citing the change in borrower’s risk score,” he adds. Hence, it would be wise to enquire with your bank and ensure that factors that will constitute a ‘substantial’ change in risk scoring are mentioned in the loan contract.
Better still, look for banks where the interest rates are transparently linked to easily-verifiable credit score. For example, Union Bank charges 8.45% if the borrower’s credit score is over 750. If it’s below this floor, the borrower will have to shell out 10 bps more. “Since the purpose of this switchover is an improvement in transparency, a similar exercise in disclosing risk scoring parameters will help. Borrowers have a right to know. Banks will have to justify the reasons for any change in credit assessment,” says Kulkarni. At the moment, clarity is yet to emerge on how all how banks can decide an improvement or deterioration in risk scores. Maintaining a clean credit history and a high credit score will become increasingly important in the coming days. Banks view those with CIBIL credit scores over 750 favorably.
Switch to save
One can switch banks to avail of new rates. By paying the same EMI even after the switch, one can save substantially on interest.










